

Studies have reported that Mn poisoning results in depolarization of the mitochondria, inhibition of the respiratory chain, and increases in mitochondrial calcium concentration 11, 12, 13, 14, 15.
Manganism is a neurodegenerative condition caused by environmental exposure to toxic levels of manganese (Mn), which mimics the effects of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) 10. Studies are increasingly connecting neurodegeneration to mitochondrial dysfunction however, exact mechanisms are not yet well understood 9. Malfunctions in brain cell metabolism are thought to be in part responsible for debilitating neurodegenerative conditions 9. These differences enable the cell types to participate in metabolic coupling in vivo to support the energy demands of neuronal electrical signaling 8. These distinctions are at least partially attributed to cell types’ different expression levels of genes essential to each energy production pathway 3, 5, 6, 7. Notably, studies from primary cultures of neurons and astrocytes have asserted that neurons primarily generate energy through mitochondrial processes including the tri-carboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, while astrocytes also produce significant levels of ATP through glycolysis 3, 4, 5, 6. Different brain cell types have distinct metabolic profiles allowing them to play complementary functions in supporting brain metabolism 3. Proper glucose metabolism is responsible for both maintaining baseline brain electrophysiology and enabling spontaneous brain activity 2. The brain is an energetically demanding organ in spite of only making up 2% of the body’s mass, it is responsible for 20% of its energy usage 1. These results exhibit TPEF’s utility for characterizing detailed metabolic changes of different brain cell types in response to neurotoxins. Astrocytes showed a decrease in bound fraction, possibly due to a shift towards glycolytic metabolism in response to impaired respiration. Furthermore, NAD(P)H fluorescence lifetime imaging revealed an increase in bound NAD(P)H fraction upon Mn treatment for neurons, consistent with enhanced apoptosis.
However, the manner in which the redox distributions was affected was distinct for the two cell types. When treated with Mn, both cell types exhibited redox ratio shifts consistent with increased oxidative stress.
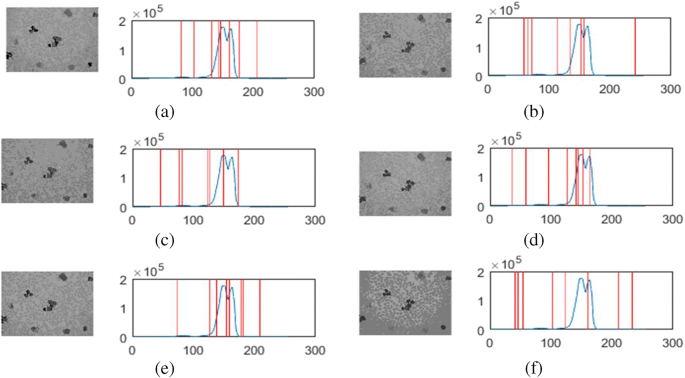
Histograms of pixel-wise optical redox ratio, defined as FAD/(FAD + NAD(P)H), revealed three distinct redox distributions and significant differences in their relative weights between astrocytes and neurons. We employed TPEF to study the metabolism of primary rat astrocyte and neuronal cultures under normal growth conditions and in response to manganese (Mn) treatment. Two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) imaging is a non-destructive, high-resolution technique for studying cell metabolism via endogenous fluorescence of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate) (NAD(P)H) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). As neurodegenerative conditions are increasingly linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, methods for studying brain cell metabolism at high spatial resolution are needed to elucidate neurodegeneration mechanisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
